Neuroticism Test: Understanding Your Big Five Personality Results
November 27, 2025 | By Alicia Campos
Have you ever taken a personality test and wondered, “What does my neuroticism score actually mean?” The Neuroticism Test helps answer that exact question. Neuroticism—one of the five core personality dimensions in psychology’s widely recognized Big Five model—powerfully shapes how we experience emotions, cope with stress, and perceive the world. When you take a Neuroticism Test, your results reveal how your score interacts dynamically with other traits like Extraversion and Conscientiousness. In this guide, we’ll break down how psychologists interpret this trait, explain what your test results reveal, and show you how to apply these insights for personal growth. Ready to decode your unique personality profile? Try our free Neuroticism Test to get started with your personalized analysis today.
What Is Neuroticism in the Big Five Personality Model?
The Big Five (Openness, Conscientiousness, Extraversion, Agreeableness, Neuroticism) is psychology’s most empirically validated personality framework. Unlike outdated models like Myers-Briggs, it measures traits on spectrums rather than binary types, offering a more nuanced understanding of human behavior.
1. The Scientific Origins of Neuroticism as a Core Trait
Psychologists define neuroticism as a tendency toward negative emotional states like anxiety, sadness, or irritability. Grounded in decades of research, this trait reflects our baseline sensitivity to stress and perceived threats. High scorers often exhibit emotional reactivity—stronger responses to challenges—while low scorers typically remain calm under pressure.
2. Key Characteristics of High vs. Low Neuroticism
-
High Neuroticism: Frequent mood swings, heightened worry, and rumination.
-
Low Neuroticism: Emotional resilience, optimism, and steady stress responses. Neither extreme is “better”—each presents unique strengths. For example, highly neurotic individuals often excel at risk assessment, while their calmer counterparts may handle crises more effectively.

3. How Neuroticism Differs from Clinical Anxiety
While neuroticism overlaps with anxiety tendencies, it’s not a mental health disorder. Think of it as a personality predisposition rather than a diagnosis. Our emotional stability test measures this trait spectrum to help you understand your natural emotional style—not to pathologize it.
Neuroticism and Extraversion: The Introvert’s Paradox
Your neuroticism score gains deeper meaning when combined with Extraversion—the trait governing social energy and outward engagement.
1. High Neuroticism + Low Extraversion: The Socially Anxious Thinker
This blend often manifests as social hesitation and overanalysis. While deeply thoughtful, these individuals may avoid gatherings due to fear of judgment. Tip: Small-group interactions often feel safer than large events.
2. High Neuroticism + High Extraversion: The Socially Engaged Worrier
Here, emotional sensitivity pairs with strong social drive. These individuals crave connection but may overanalyze interactions (“Did I offend them?”). Our test’s AI-powered feedback helps identify triggers for such rumination.
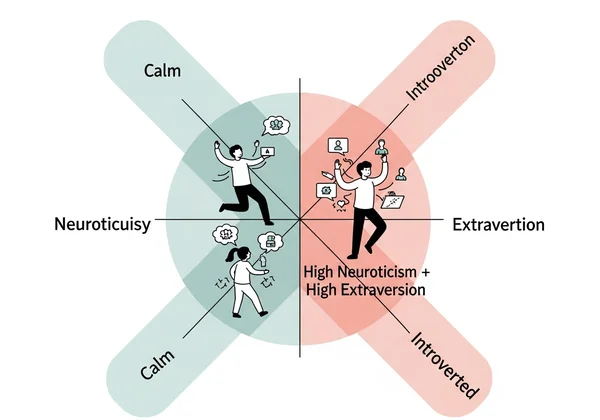
3. Low Neuroticism + High Extraversion: The Resilient Social Butterfly
Low emotional reactivity combined with social confidence creates natural networkers who thrive in dynamic environments—think educators or event planners.
Neuroticism and Conscientiousness: The Productivity Dilemma
When neuroticism intersects with Conscientiousness (organization/goal-orientation), it creates fascinating work-style patterns.
1. High Neuroticism + High Conscientiousness: The Anxious Perfectionist
This common professional profile drives meticulous work but risks burnout. Recognize yourself? Our Big Five assessment includes strategies for balancing standards with self-compassion.
2. High Neuroticism + Low Conscientiousness: The Creative Underachiever
Gifted but distractible, these individuals often struggle to complete projects due to self-doubt. Structured routines and progress-tracking tools can help unlock their potential.
3. Low Neuroticism + High Conscientiousness: The Calm Achiever
A coveted combination for high-pressure roles (e.g., surgeons, pilots), pairing methodical focus with stress resilience.
Neuroticism and Openness to Experience: The Creative Intensity
Openness reflects imagination and intellectual curiosity—traits that interact uniquely with neuroticism.
1. High Neuroticism + High Openness: The Intense Creative
Artists, writers, and innovators often fit this profile. Their emotional depth fuels creativity but may lead to overthinking. Channeling feelings into art or journaling can be therapeutic.
2. High Neuroticism + Low Openness: The Traditional Worrier
Preferring routine over novelty, these individuals often fixate on “what could go wrong” in familiar settings (e.g., family logistics). Cognitive-behavioral techniques can help manage catastrophic thinking.
Neuroticism and Agreeableness: The Social Sensitivity Balance
Agreeableness (empathy/cooperation) softens or intensifies neuroticism’s social impact.
1. High Neuroticism + High Agreeableness: The Overly Accommodating Person
These kind-hearted individuals often prioritize others’ needs to avoid conflict—sometimes at their own expense. Learning to set boundaries is key.
2. High Neuroticism + Low Agreeableness: The Defensive Critic
Quick to perceive slights, this combination may lead to contentious relationships. Mindfulness practices can help pause before reacting.
Putting It All Together: Your Unique Trait Matrix
No single trait defines you. It’s the interplay between neuroticism and your other scores that paints your full personality portrait. For instance:
-
A High Neuroticism + High Openness + High Agreeableness profile might describe a passionate advocate who feels others’ pain deeply
-
A Low Neuroticism + High Conscientiousness + Moderate Extraversion profile could fit a disciplined engineer who thrives on logical problem-solving
Curious where you fall? Take our 5-minute assessment to visualize your trait combinations and receive actionable insights tailored to your results.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What does a high neuroticism score mean in the Big Five model?
It indicates a natural tendency to experience negative emotions more intensely or frequently. However, it doesn’t equate to mental illness—many high scorers channel this sensitivity into creativity, empathy, or meticulous planning. Our free personality report explains your score in everyday contexts.
2. Can neuroticism change over time?
Yes! While partly genetic, research shows that therapy, mindfulness, and lifestyle changes can reduce neurotic tendencies. Tracking your score annually with our tool helps monitor progress.
3. Is neuroticism always a weakness?
Absolutely not. In controlled amounts, it enhances preparedness (e.g., saving for emergencies) and creativity. Our AI Analysis upgrade details how to harness your specific neuroticism profile strategically.
4. How does your test compare to clinical assessments?
Like all Big Five tools, ours measures general personality traits—not disorders. For clinical concerns (e.g., severe anxiety), consult a licensed therapist. We provide a detailed disclaimer to clarify this distinction.
5. Why test neuroticism alongside other traits?
Context matters! A moderately high neuroticism score paired with high Conscientiousness suggests different strengths/challenges than the same score with low Agreeableness. Get your complete profile by starting the test now.
Your neuroticism score is just one piece of your personality puzzle—but when combined with your other traits, it reveals powerful insights about your relationships, career fit, and growth opportunities. Ready to see the full picture?
🔍 Discover Your Big Five Profile in Minutes: ✅ Free instant score report ✅ Optional AI-generated strengths/weaknesses analysis ✅ 15+ languages supported ✅ 100% confidential
Take the Neuroticism Test Understand yourself to grow yourself.